Introduction
This article introduces the problem of slagging caused by laser cutting focus and how to adjust the focus position to solve it. In addition, a new cutting process called raysoar gas-mixed cutting is also introduced. This process can achieve clean cutting by removing oxide, burrs, and slag, and has lower cost than liquid nitrogen cutting and higher revenue than oxygen cutting. It is a laser cutting gas supply solution worth considering.
What is laser cutting dross
Lasers are known as the “fastest knife” in the industry because laser cutting uses the high temperature of the laser beam to cut through metal like butter. However, in actual sheet metal cutting processes, many of our sheet metal processing friends often encounter various slagging phenomena.
There are many reasons for cutting slagging, such as the auxiliary gas pressure being too high or too low during laser cutting, which causes too much or too little heat input, both of which can cause cutting slagging. In addition, laser drilling or small-area cutting may also cause slagging problems due to the small heat dissipation space and too much heat concentration.
Although slagging is inevitable, we can troubleshoot and debug to meet different customers’ requirements and standards for the quality of the cut product cross-section. Today, raysoar engineers will deeply analyze the causes of slagging problems from a professional perspective and how to systematically troubleshoot and debug to solve slagging problems. If you still can’t solve the slagging problem, you can contact raysoar.
The following is an analysis of the reasons for the slag caused by laser cutting from four aspects.
Cause 1:Slag caused by laser output power
During the actual laser cutting process, both excessive and insufficient laser output power can cause varying degrees of slagging problems. For example, when cutting metal sheets of the same thickness and material, setting the laser output power too high will result in a larger melting cut seam on the cutting section, which cannot achieve the “bright cutting” effect that is commonly used in our industry. On the other hand, setting the laser output power too low may lead to incomplete cutting, resulting in cutting spatters, and even scars on the cutting section.
Raysoar’s solution is to set the appropriate laser output power according to the material type of the cutting plate to achieve a “bright” cutting effect.
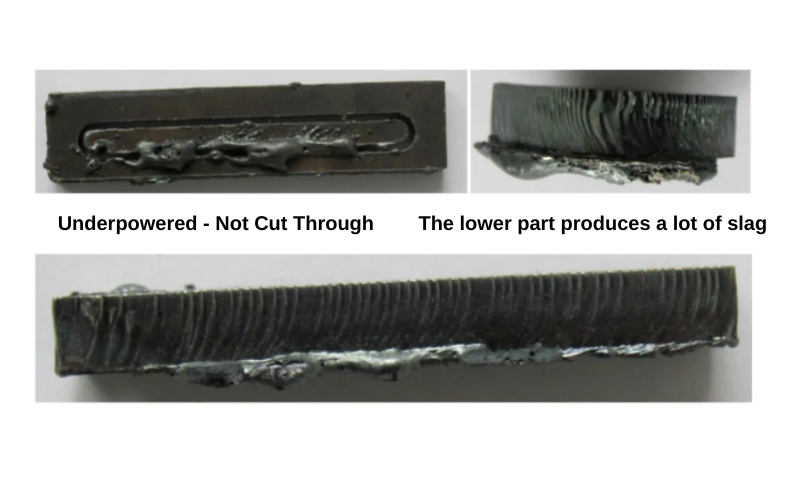
Cause 2:Dross caused by laser cutting auxiliary gas
In the process of laser cutting, auxiliary gas is needed for cutting. Commonly used auxiliary gases include oxygen, compressed air, nitrogen (liquid nitrogen), and rare gases. The main function of the auxiliary gas is to blow away the molten slag generated in real time during the cutting process, and to achieve rapid cooling of the cutting heat-affected zone by the gas.
In the cutting process of the vast majority of metal sheet processing, we often choose oxygen as the cutting auxiliary gas because oxygen is a reactive gas that can oxidize the metal surface and improve cutting efficiency. However, if the auxiliary gas pressure is too high during the cutting process, there will be gas eddy currents on the surface of the sheet that cannot be observed by the naked eye. This eddy current phenomenon will directly affect the ability of the auxiliary gas to blow away the molten material in real time, ultimately causing the cutting seam to widen, the cutting section to be rough, and slag hanging. Conversely, if the auxiliary gas pressure is too low during the cutting process, the cutting auxiliary gas cannot blow away the molten material quickly and efficiently, which directly causes the cutting melt to adhere and slag hang on the underside of the cutting sheet.
The solution provided by Raysoar is to set the appropriate auxiliary gas pressure according to the thickness of the cutting sheet to achieve high-quality cutting results.
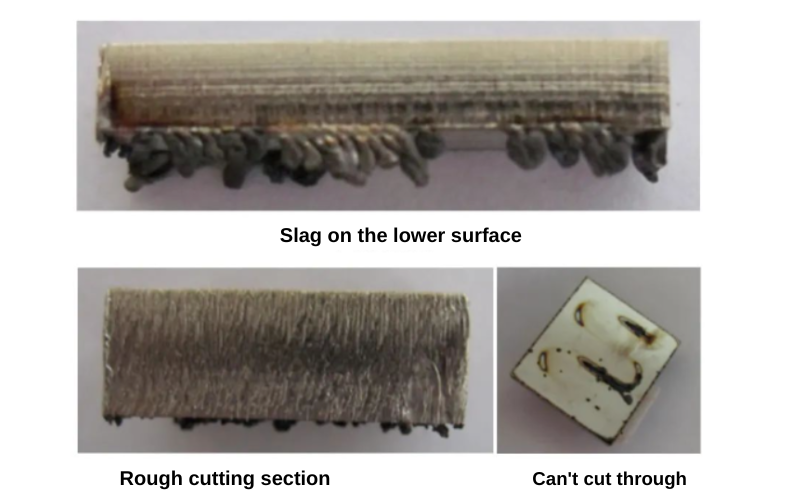
Cause 3:Dross caused by laser cutting speed
From a profit perspective, service providers usually prioritize cutting speed because it directly affects cutting efficiency. However, in the laser cutting process, we cannot blindly pursue cutting speed, as both too fast or too slow can result in cutting section defects that do not meet customer requirements.
When laser cutting, we should determine the appropriate cutting speed based on the material and thickness of the cutting plate. The figure below shows the cutting slag defect caused by improper cutting speed selection.
Raysoar’s solution is to adjust the cutting speed in a timely manner according to the cutting plate and thickness. Method for adjusting cutting speed: In general laser cutting, the cutting “flame” affected by the beam spreads from top to bottom. If the cutting “flame” is skewed, it can be judged that the cutting speed is too fast; if the cutting “flame” does not spread and is minimal, it can be judged that the cutting speed is too slow. Only with moderate cutting speed, the cutting surface will exhibit a more stable drag line, and there will be no melted residue in the lower part of the cutting surface.
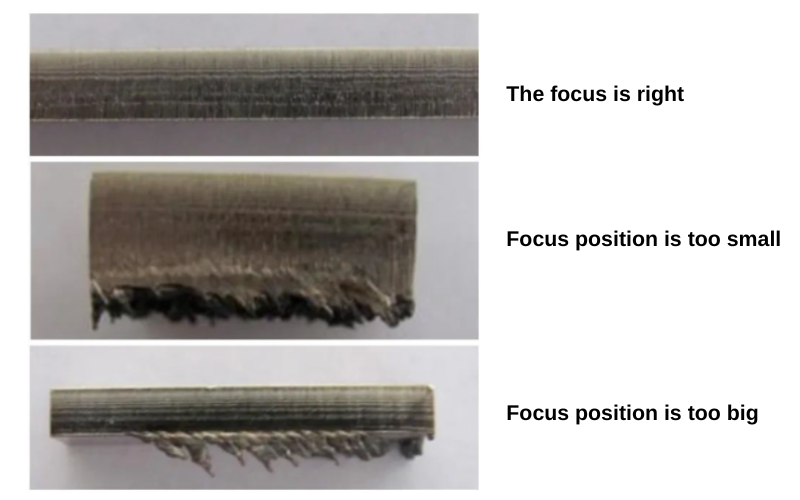
Cause 4:Dross caused by laser cutting focus
The laser cutting focus position refers to the distance between the laser focus and the surface of the workpiece. The cutting focus has a direct impact on the roughness of the cutting section, the width of the cutting seam, and the cutting slope.
If the focus position is too low, it will cause the heat absorbed by the lower end or lower surface of the cut sheet to increase. Under the premise that the cutting speed and the auxiliary gas pressure remain unchanged, the material near the cutting seam of the cut sheet will appear liquid on the lower surface of the sheet and will adhere to the workpiece in a spherical shape once it cools down. If the focus position is too high, it will cause the heat absorbed by the lower end or lower surface of the cut sheet to decrease, which may cause the material in the cutting seam of the sheet to not completely melt. This will cause sharp, small residues to adhere to the lower surface of the sheet. Adjusting the appropriate cutting focus position and making moderate adjustments according to the actual focus offset position generated during the laser cutting process can solve this problem.
Raysoar’s solution to laser cutting dross
After troubleshooting slagging issues through the aforementioned steps, if the problem persists, consider learning about Raysoar Gas-Mixed Cutting, a new cutting technology. Raysoar Gas-Mixed Cutting, also known as Raysoar Fine Cutting, is a completely new cutting process that can replace air, oxygen, and liquid nitrogen. This process compresses air with an air compressor, filters out impurities, removes water through a refrigerated dryer (or suction dryer), and produces nitrogen through a pressure swing adsorption process. Equipment required includes an air compressor, air storage tank, filter, refrigerated dryer (or suction dryer), nitrogen generator, relevant control system, and instruments.
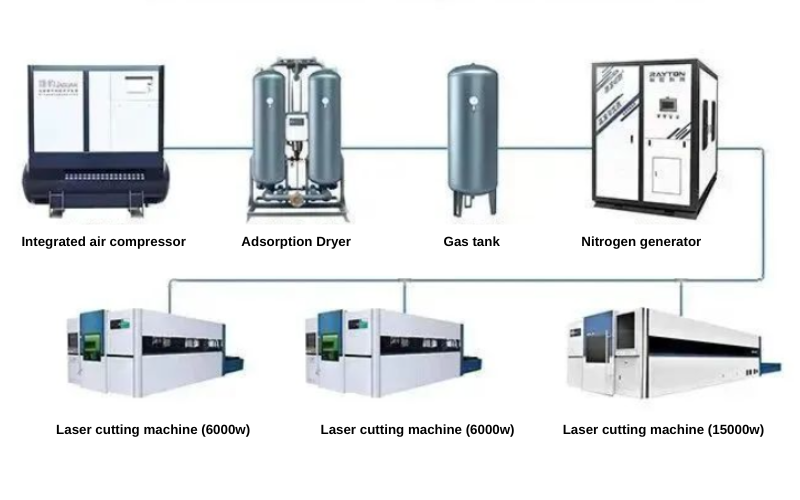

The following compares the raysoar solution with other solutions in terms of efficiency and cost analysis
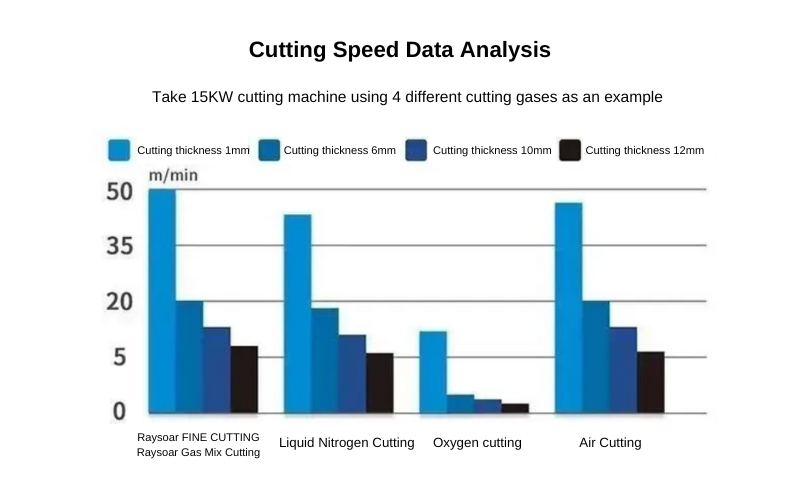
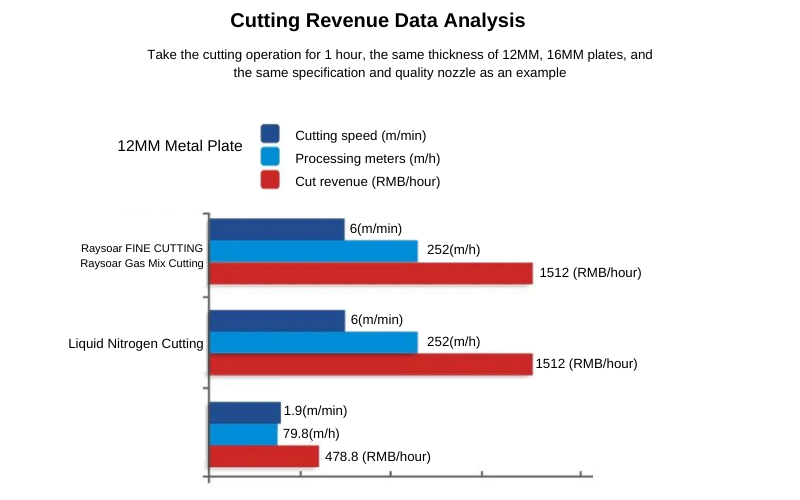
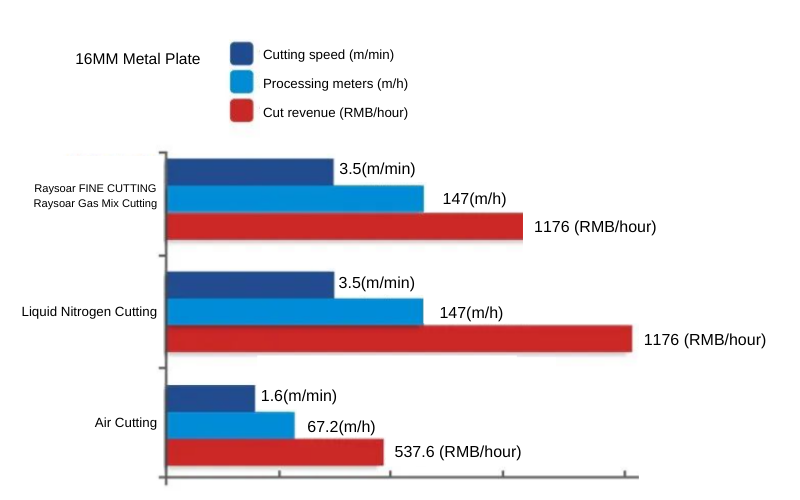
Analysis of Cutting Speed Data
Taking a 15KW cutting machine using four different cutting gases as an example, the cutting thicknesses are 1mm, 6mm, 10mm, and 12mm. For fine cutting, compared with liquid nitrogen cutting, oxygen cutting, and air cutting, it has faster cutting speed and higher efficiency for fine cutting.
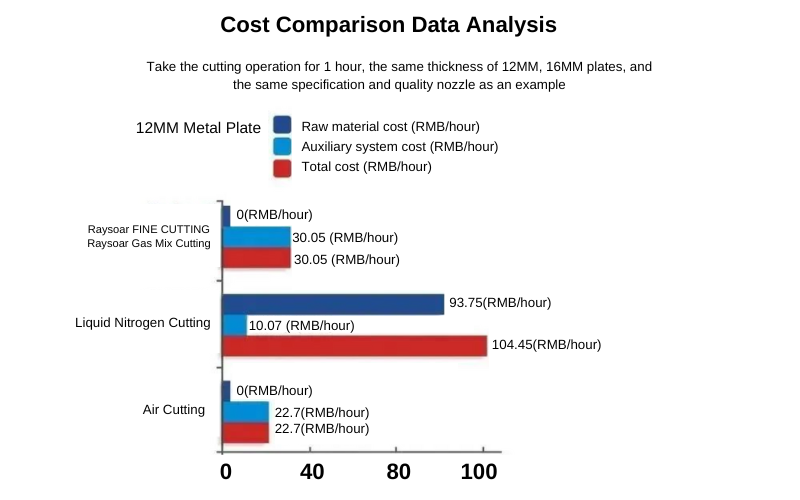
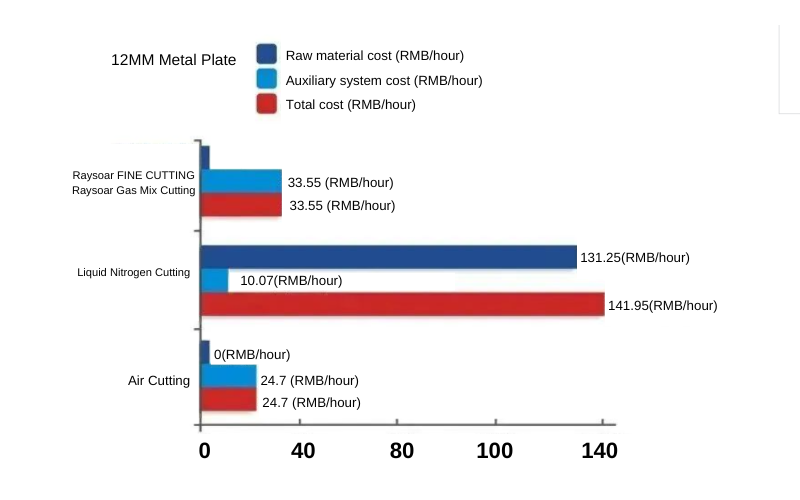
Cost Comparison Data Analysis
Taking a cutting operation duration of 1 hour, the same thickness of 12mm and 16mm plates, and the same specification and quality nozzle as an example. The cost of fine cutting 12mm plate is 30.05 yuan/hour, liquid nitrogen cutting is 104.45 yuan/hour, and air cutting is 22.7 yuan/hour. Therefore, compared to liquid nitrogen cutting, the cost of raysoar gas-mixed cutting is saved by 71%, and the cost is only 32% higher than air cutting. The cost of fine cutting 16mm plate is 33.55 yuan/hour, liquid nitrogen cutting is 141.95 yuan/hour, and air cutting is 24.7 yuan/hour. Therefore, compared to liquid nitrogen cutting, the cost of raysoar gas-mixed cutting is saved by 76%, and the cost is only 36% higher than air cutting.

Conclusion
- From the cost data analysis, the cost of raysoar gas-mixed cutting is much lower than liquid nitrogen cutting, slightly higher than air cutting, but it can achieve clean cutting with oxide removal, burr removal and slag removal.
- From the cutting revenue analysis, the revenue of raysoar gas-mixed cutting is much higher than oxygen cutting and can perfectly replace oxygen cutting.
- In summary, from multiple dimensions such as cutting efficiency, cutting quality, cutting cost, and cutting revenue, the gas supply scheme of raysoar gas-mixed cutting is indispensable for your laser cutting machine in choosing a gas supply method, as demonstrated by the data.
Share:
Contact us





